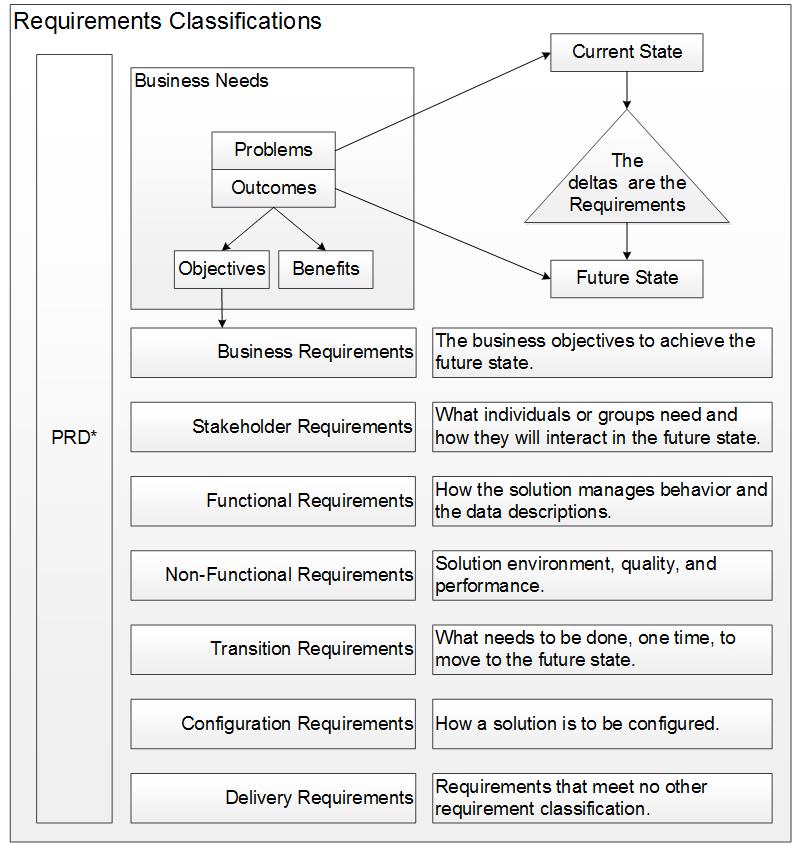
The highest order of description for an initiative’s requirements is the business need, made up of the problem or opportunity, and the desired outcome. Business Outcome Analysis extends business needs with objectives and benefits.
Good requirements governance should reduce ambiguity. The term “high level” has been described as another way to say “open to interpretation”, in other words, with ambiguity. Therefore, there are no high level requirements. The term is ambiguous and should not be used in requirements management.
The BABOK® Guide describes the following requirements classifications:
- Business requirements: statements of goals, objectives, and outcomes that describe why a change has been initiated. They can apply to the whole of an enterprise, a business area, or a specific initiative.
- Stakeholder requirements: describe the needs of stakeholders that must be met in order to achieve the business requirements. They may serve as a bridge between business and solution requirements.
- Solution requirements: describe the capabilities and qualities of a solution that meets the stakeholder requirements. They provide the appropriate level of detail to allow for the development and implementation of the solution. Solution requirements can be divided into two sub-categories:
- functional requirements: describe the capabilities that a solution must have in terms of the behaviour and information that the solution will manage
- non-functional requirements or quality of service requirements: do not relate directly to the behaviour of functionality of the solution, but rather describe conditions under which a solution must remain effective or qualities that a solution must have.
- Transition requirements: describe the capabilities that the solution must have and the conditions the solution must meet to facilitate transition from the current state to the future state, but which are not needed once the change is complete. They are differentiated from other requirements types because they are of a temporary nature. Transition requirements address topics such as data conversion, training, and business continuity.
There are other classes of requirements not described in the BABoK, such as configuration and infrastructure.
All requirements can be refereed to as Delivery Requirements.
These can be illustrated as:
- PRD – Project Requirements Document (see Universal Requirements Template)
Concepts: BACCM Terms Classifications Stakeholders Requirements and Designs
